The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structured process that guides the creation, maintenance, and evolution of software. It involves a series of well-defined phases, each with specific activities and deliverables, ensuring a systematic and efficient approach to software development.
This video explains the seven key phases of the SDLC, including planning, design, and testing:
Here’s a breakdown of the typical phases:

1. Planning: This initial phase involves gathering requirements, defining project scope, and creating a high-level plan. It’s crucial to understand the client’s needs, establish project goals, and identify potential risks.
This video provides an introduction to the SDLC and its phases, starting with planning requirements:
2. Requirements Analysis: This phase focuses on translating the high-level requirements into detailed specifications. It involves analyzing user needs, defining functional and non-functional requirements, and creating a detailed document outlining the system’s behavior.
3. Design: The design phase involves creating a blueprint for the software. This includes designing the system architecture, database schema, user interface, and algorithms.
4. Implementation (Coding): This is where the actual software development takes place. The design specifications are translated into code, and the software modules are built and integrated.
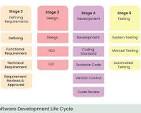
5. Testing: Thorough testing is crucial to ensure the software meets the defined requirements and is free of defects. This phase includes various types of testing, such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing.